Grammar the Montessori (Fun) Way!
The study of words, grammar, is all about understanding how words function and how they relate to each other in a sentence. In essence, grammar represents the rules that we use, either consciously or unconsciously, as we speak and write. And in Montessori classrooms, grammar is incredibly fun!
In early childhood, children effortlessly absorb the language(s) in their environment, including the grammatical conventions people around them use. So in our primary classrooms, we first offer a series of games to introduce children to the functions of words.
The Games
The games provide a sensorial experience of the function of each part of speech. For example, when we invite children to the “article game,” we play around with asking for items using either the article “the” or “a” depending upon if we are thinking of a definite object (like the laundry basket) or an indefinite one (like a red pencil, which could be any of the red pencils in the classroom).
Or with the “preposition game,” we give commands using prepositions (words that show relationship) such as: “Put your hands on your stomach.” “Put your hands under the chair.” “Put your hands behind your back.” Each time we only change the preposition, so that children experience what happens when we change that one word.
Children also love the “verb game” and the “adverb game” because they get to engage in all sorts of actions that can get more and more complex depending upon the series of commands from “run” and “skip” to “walk loudly” or “tiptoe angrily” to multi-step requests like “Walk to a friend. Say hello to the friend. Come back to me. Tell me the friend’s name.”
Our early childhood children consider these games to be delightful and often request them again and again!
A “Feel” for Language
Eventually, children in our early childhood classrooms move on to grammar-based activities that involve a great deal of reading. Using little paper slips and objects, we present a variation of the grammar games that isolate the different parts of speech and help children intuit the patterns in our language. We write words and phrases on the paper slips, children read them, and label different objects or items in the classroom. We also begin introducing symbols for each part of speech.
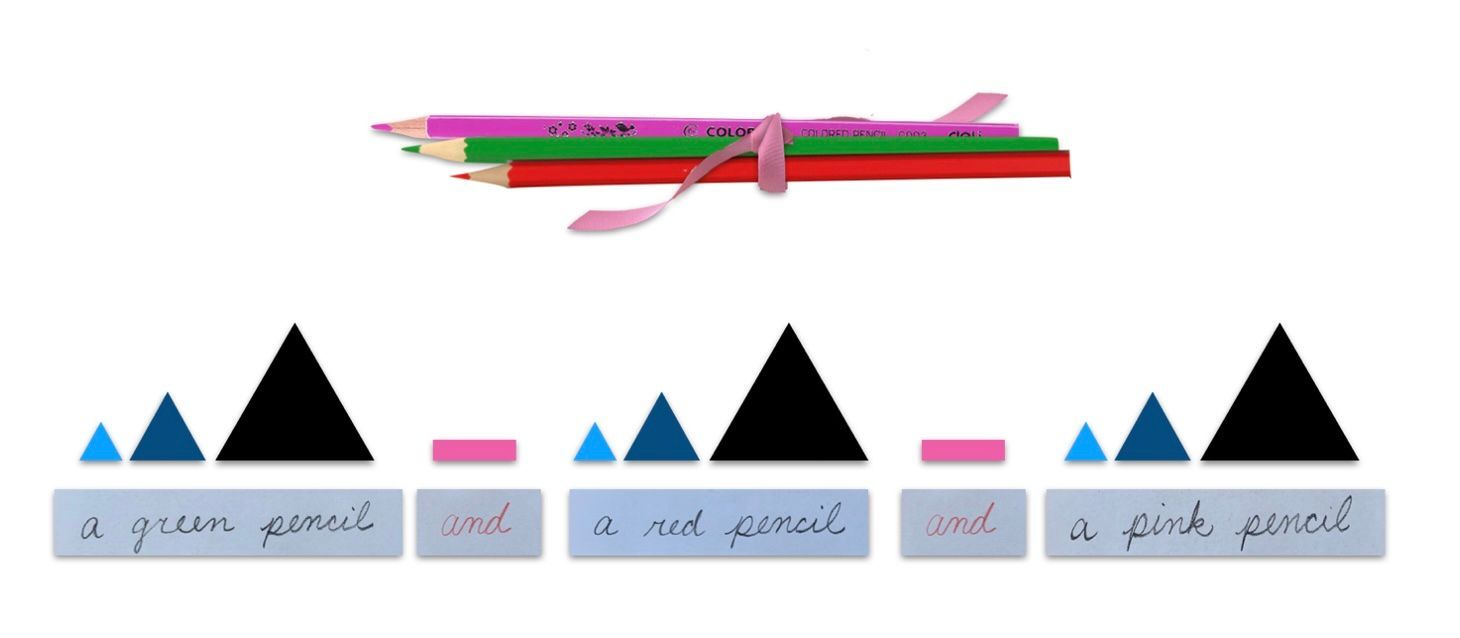
For example, by the time children have learned about nouns, articles, and adjectives, we can introduce conjunctions as words that connect. We can write little slips for individual objects (“a green pencil,” “a red pencil,” “a pink pencil”). The children collect those pencils and we connect them with a pink ribbon. We also highlight the word that connects each of the objects (“and”) by writing it in red. Finally, we add each of the symbols that represent each part of speech.

Because children of this age are very tuned into syntax, they quickly develop a “feel” for how words are used in sentences. A great example of this is how young children might say, “I runned as quickly as I could.” Just through experience, they are able to identify how past tense is formed by adding “ed” to the verb. All that is needed next are opportunities to learn about how some words don’t follow that particular rule.
Systematic Study
In the elementary years, we embark on a systematic study of the different types of rules, such as those that direct the formation of the past tense. In addition to learning about suffixes (such as “ed”) that affect tense, elementary students learn about auxiliary verbs and even study the mood and voice of verbs. The children also discover that our irregular verbs have a historical origin. In fact, many of the seeming inconsistencies of our language have a fascinating historical story!
For that reason, whenever possible in elementary, we link grammar to history. The word grammar, for example, comes from the ancient Greek term grammatike tekhne, which means “art of letters.”
As we embark on “the art of letters,” our elementary children dive into several disciplines, including morphology (the structure of words), syntax (the arrangement of words), phonology (the pronunciation of words), semantics (the meaning of words), and etymology (the history of words). We distill these disciplines into three main areas: word study, parts of speech, and sentence analysis.
The Grammar Boxes
In next week’s blog, we’ll highlight a deeper exploration of how one material, the beloved Grammar Boxes, connects these key areas of study. In addition to helping children understand how words have a function to perform and how the sequence of words and surrounding words determine the function, the Grammar Boxes also support the study of words and lay the foundation for sentence analysis.
Our grammar lessons and presentations are quite lively and involve a great deal of activity. We’d love to have you schedule a visit to come see this grammar work in action!






