Stages of Development Series: Infancy

Imagine education from a fresh perspective—one that sees children not as empty vessels waiting to be filled but as whole individuals embarking on a lifelong journey of self-formation. From the moment of birth, children are driven by powerful internal forces that guide their growth and help them adapt to their unique time, place, and culture. This remarkable ability to evolve and adapt is a defining trait of our human species.
The Montessori approach to education is built upon this profound understanding of human development. Dr. Maria Montessori dedicated her life's work to observing how children grow and change over time, identifying key developmental stages that shape their path to maturity. Through her scientific observations, she identified four distinct planes of development, each with its own unique characteristics and needs.
In this four-part blog series, we’ll explore each of these four stages—birth to age six, six to twelve, twelve to eighteen, and eighteen to twenty-four—unpacking how Montessori education adapts to support children’s evolving needs at every phase of growth. By understanding these developmental stages, we can better support young people on their journey to becoming capable, independent, and fulfilled individuals.
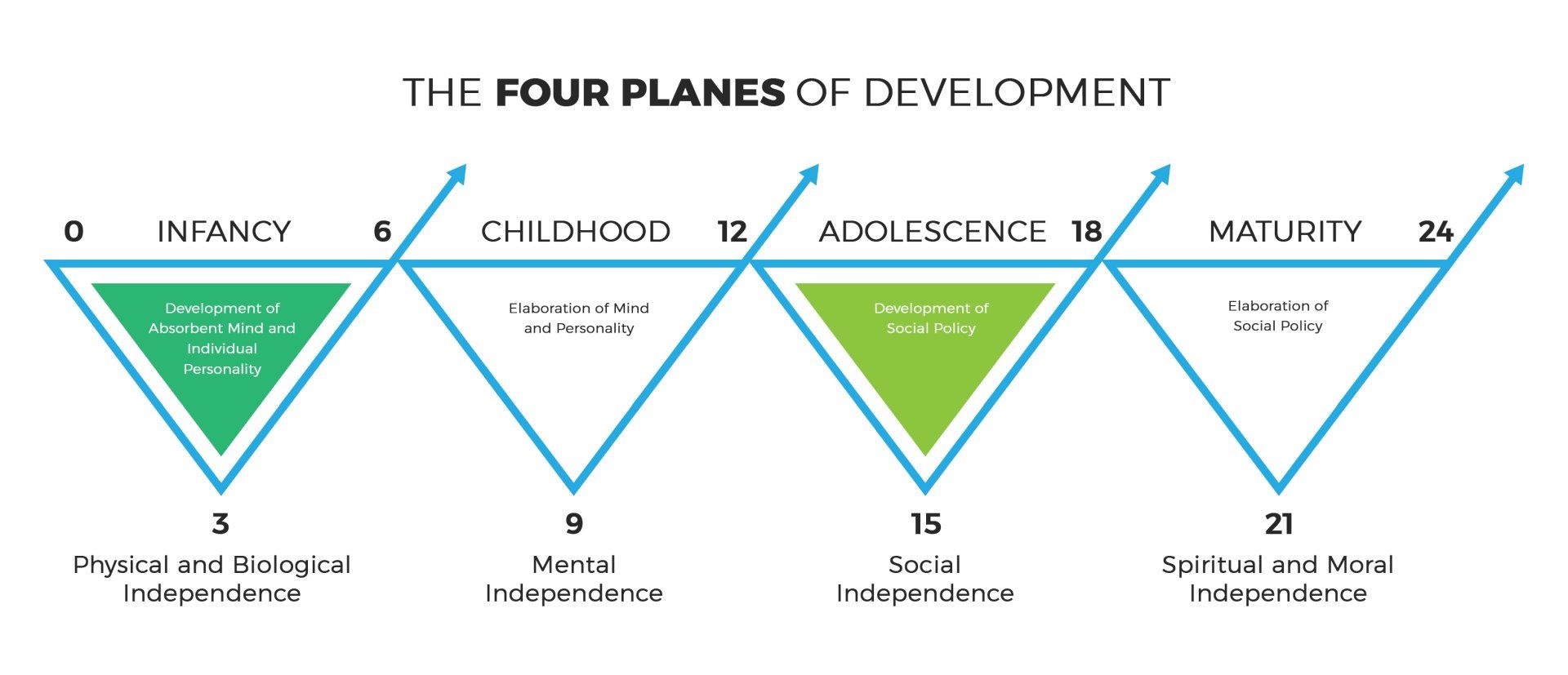
Infancy (Birth to Age Six)
The first plane of development is an extraordinary period of psychological and physical growth. Newborns enter the world entirely dependent, unable to move or communicate. Yet, within just six years, they are walking, talking, and asserting their independence with intellect and will.
Characteristics of the First Six Years
During this transformative stage, children require ample sleep to support their rapid development. However, when they are awake, their curiosity knows no bounds. They explore their surroundings with boundless energy, using their senses to touch, smell, taste, hear, and examine everything in their environment.
Conquest of Independence
One of the primary goals during this stage is achieving functional independence. Children are eager to take care of their own needs and are naturally inclined to observe and imitate the actions of adults. The mantra of children at this stage is: “Help me do it myself!”
Sensitive Periods
Children in the first plane experience sensitive periods—windows of opportunity when they are uniquely receptive to acquiring essential skills.
Movement: Young children need movement to develop brain-body integration.
Order: They crave order to make sense of their surroundings, learning what happens and how objects are used.
Language Acquisition: This is a critical period for language development, during which children absorb words and speech patterns effortlessly.
These sensitivities drive children’s development, shaping their understanding of the world.
Observable Milestones
One of the most profound achievements in this phase is the acquisition of spoken language. Talking to newborns, for example, stimulates vocal cord development, and astonishingly, their vocal cords vibrate when adults speak to them. From being essentially mute at birth, toddlers can have a vocabulary of around 200 words by age two and an impressive 10,000 words by the end of this phase. This makes it essential to provide a language-rich environment during these formative years.
Physically, this period is one of monumental growth. Children progress from being immobile to sitting, crawling, walking, speaking, and independently eating. As adults, we must be mindful about supporting rather than hindering this development. We want to offer rather than limit growth opportunities for our children!
The Sub-Planes: Ages 0 to 3 and Ages 3 to 6
The first plane of development can be divided into two distinct sub-phases:
Ages 0 to 3: Children’s development is largely unconscious, driven by innate forces. During this phase, children absorb the world around them and do so without any filters. It’s important during this time that adults respect children’s natural developmental path without imposing external motivations.
Ages 3 to 6: During these years, children become more consciously aware of their actions and motivations. This is when we see the emergence of children’s willpower and the powerful drive to classify and understand their environment. Children become more conscious learners.
As they grow, children naturally identify patterns, similarities, and differences based on their experiences. They construct their understanding of the world from scratch, and active experiences in their environment play a crucial role in shaping their cognitive development.
Social Development in the First Plane
During their first three years, children form strong bonds with their primary caregivers and family, finding comfort in a small social circle. They prefer solitary exploration and engage in parallel play.
By age three, children seek a broader social experience beyond the family. They require opportunities to interact with peers and engage in community life, which fosters independence and social development.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Providing the right environment is crucial to supporting children during their early years. Key elements of an optimal environment include:
A Secure Home: A safe and loving home helps children build trust and confidence in the world around them.
Freedom to Explore: Children need space and opportunities to move and explore safely, both indoors and outdoors.
Language Exposure: A rich linguistic environment helps children build vocabulary and develop confidence in self-expression.
Participation in Daily Life: Involvement in practical life activities helps children develop independence and a sense of belonging.
Cultural Experiences: Exposure to family traditions, rituals, and cultural practices helps children adapt to their culture and understand their place within it.
As children develop over the course of this stage of life, they also benefit from being part of a social community and, in the process, learn valuable lessons about cooperation, sharing, and responsibility.
By understanding the characteristics and needs of the first plane of development, we can create environments that nurture children’s natural growth, independence, and exploration. We invite you to visit our school to see for yourself how a prepared environment can meet the needs of our youngest children!






